|
 |
Graphs and Charts for Light Speed, Planck's Constant and Mass
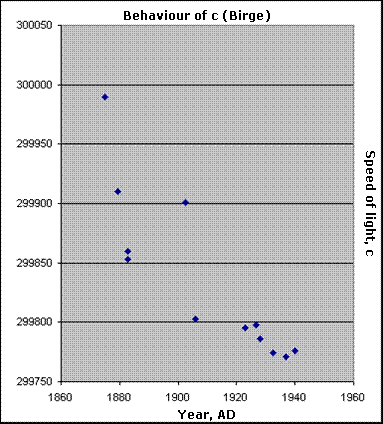
The graphs on this page were formulated to show the consistent trends in light speed, Planck's constant, and mass as measured and accepted scientifically in the years indicated. The light speed measurements are those accepted by Professor Raymond Birge until 1941 and may be referenced, along with many more, in the abundance of charts and footnotes in Atomic Constants, Light and Time.
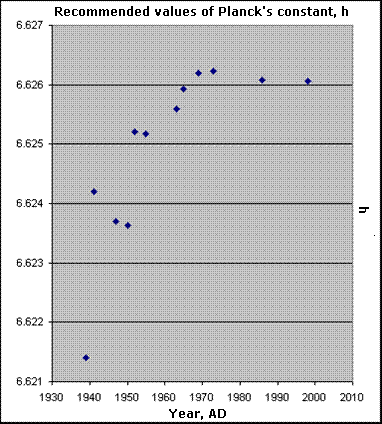
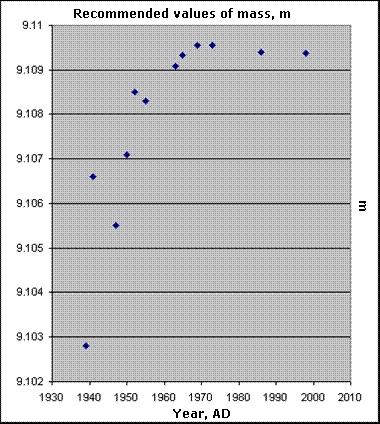
It will be noticed that there is a leveling off, or even slight reversal, of all three sets of measurements about 1970-1972. The explanation for this may be found in "Summary of Zero Point Energy (ZPE) phenomena," as well as in the section on the "Origin of the Zero Point Energy" in Data and Creation.
References for the Planck particle and mass measurements are at the bottom of this page.
|
 |
 |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
 |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
References by year for both h and m in the above charts:
1939 -- Dunnington, F.G., The Atomic Constants, Reviews of Modern Physics, 11 (2), 65-83, Apr. 1939
1941 -- Birge, R.T., A New Table of Values of the General Physical Constants, Reviews of Modern Physics, 13 (4), 233-239, Oct. 1941
1947 -- DuMond, J.W.M., and E.R. Cohen, Our Knowledge of the Atomic Constants F, N, m and h in 1947, and of Other Constants Derivable Therefrom, Reviews of Modern Physics, 20 (1), 82-108, Jan. 1948
1950 -- Bearden, J.A., and H.M. Watts, A Re-Evaluation of the Fundamental Atomic Constants, Physical Review, 81, 73-81, Jan. 1, 1951
1952 -- DuMond, J.W.M., and E.R. Cohen, Least Squares Adjustment of the Atomic Constants, 1952, Reviews of Modern Physics, 25 (3), 691-708, Jul. 1953
1955 -- Cohen, E.R., et al., Analysis of Variance of the 1952 Data on the Atomic Constants and a New Adjustment, 1955, Reviews of Modern Physics, 27 (4), 363-380, Oct. 1955
1963 -- Cohen, E.R., and J.W.M. DuMond, Present Status of our Knowledge of the Numerical Values of the Fundamental Constants, p.152-186, Proceedings of the Second International Conference on Nuclidic Masses, Vienna, Austria, July 15-19, 1963, W.H. Johnson, Jr., editor, Springer-Verlag, Wien, 1964
1965 -- Cohen, E.R., and J.W.M. DuMond, Our Knowledge of the Fundamental Constants of Physics and Chemistry in 1965, Reviews of Modern Physics, 37 (4), 537-594, Oct. 1965
1969 -- Taylor, B.N., W.H. Parker, D.N. Langenberg, Determination of e/h Using Macroscopic Quantum Phase Coherence in Superconductors: Implications for Quantum Electrodynamics and the Fundamental Physical Constants, Reviews of Modern Physics, 41 (3), 375-496, Jul. 1969
1973 -- Cohen, E.R., and B.N. Taylor, The 1973 Least-Squares Adjustment of the Fundamental Constants, Journal of Physical and Chemical Reference Data, 2 (4), 663-718, 1973
1986 -- E.R. Cohen , B.M. Taylor, The 1986 Adjustment of the Fundamental Physical Constants, Codata Bulletin #63, Pergamum Press, Nov. 1986
1998 -- P.J. Mohr and B.N.Taylor, Codata Recommended Values of the Fundamental Physical Constants, 1998, Reviews of Modern Physics, April, 2000 http://physics.nist.gov/constants